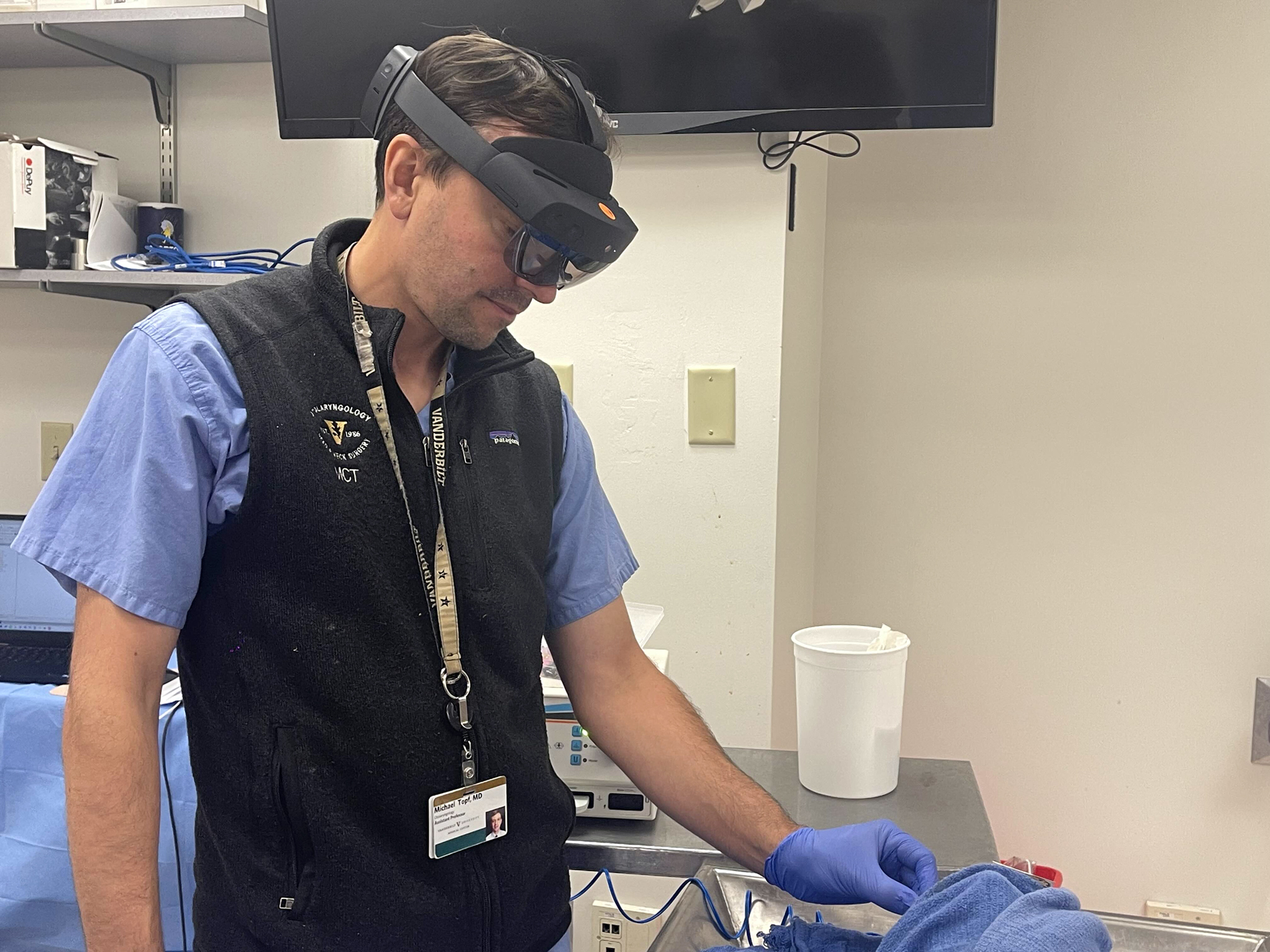
Introduction to Innovative Surgery
The medical field is consistently evolving, with recent technologies being developed to enhance patient care and treatment outcomes. One area that has seen significant advancements in recent times is surgery, particularly within the realm of tumor resection. A brand new grant is supporting the event of a head-mounted augmented reality system designed to guide surgeons during these complex procedures.
What is Augmented Reality in Surgery?
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that superimposes digital information onto the actual world, using a tool reminiscent of a headset or glasses. In the context of surgery, AR can provide surgeons with critical information, reminiscent of the situation of tumors, blood vessels, and other essential structures, in real-time. This can assist reduce the chance of complications and improve the accuracy of the procedure.
How Does the Head-Mounted System Work?
The head-mounted AR system being developed uses advanced imaging technologies, reminiscent of MRI and CT scans, to create detailed 3D models of the patient’s anatomy. These models are then superimposed onto the surgeon’s field of view, allowing them to see the situation of the tumor and surrounding structures in real-time. The system also uses machine learning algorithms to assist discover the tumor and supply guidance to the surgeon through the procedure.
Benefits of the Technology
The use of a head-mounted AR system has several potential advantages for surgeons and patients. It can reduce the necessity for traditional imaging techniques, reminiscent of fluoroscopy, which may expose patients to radiation. It also can help surgeons to raised understand the anatomy of the patient, reducing the chance of complications and improving the accuracy of the procedure. Additionally, the system can provide real-time feedback to the surgeon, allowing them to make adjustments through the procedure as needed.
Future of Tumor Resection
The development of this head-mounted AR system has the potential to revolutionize the sphere of tumor resection. By providing surgeons with real-time guidance and feedback, it may help improve patient outcomes and reduce the chance of complications. As the technology continues to evolve, it is probably going that we are going to see much more modern applications of AR within the medical field.
Conclusion
The development of a head-mounted augmented reality system to guide tumor resection is an exciting advancement in the sphere of surgery. With its potential to enhance patient outcomes and reduce the chance of complications, this technology has the potential to make a big impact on the medical community. As researchers proceed to refine and improve the system, it should be interesting to see the way it is integrated into clinical practice and what advantages it brings to patients and surgeons alike.