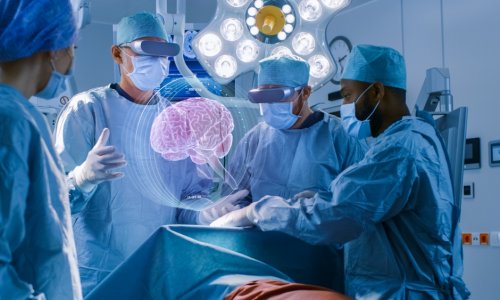
Introduction to Mixed Reality in Medical Education
Professor Dr Anders Persson from the Department of Radiological Sciences at Linköping University, Sweden, has been exploring the potential of mixed reality in medical education and training. In a recent presentation, he highlighted the advantages and challenges of using this technology to show medical students and residents.
The Challenges of Using Virtual Reality in Medical Education
Persson explained that while virtual reality (VR) could be a powerful tool for education, it has its limitations. For example, VR is a closed environment that could make it difficult to make use of for real-time clinical exams of CT or MR images. The technique of moving data from the scanner, segmenting it, and making a 3D model will be time-consuming and will not accurately represent the true thing. As a result, making a diagnosis using VR images will be difficult.
The Benefits of Mixed Reality in Medical Education
Despite the challenges of VR, Persson believes that mixed reality (MR) is a game-changer for medical education. MR allows students to interact with 3D anatomical models in a more immersive and interesting way. Multiple students can examine a model at the identical time, taking it apart layer by layer to raised understand the body’s anatomy. This technology also enables students to speak with teachers more effectively, making it a super tool for education.
Using Mixed Reality without Goggles
One of the benefits of MR is that it doesn’t require using goggles or headsets. Persson’s team uses a visualization table that permits them to take data directly from the scanner and look at it in 3D. This technology provides a more collaborative and interactive learning experience, enabling students to work together to know complex anatomical structures.
Expanding the Use of Mixed Reality to Patient Education
The advantages of MR should not limited to medical education. Persson believes that this technology will also be used to teach patients and their families about their medical conditions. By providing a more interactive and interesting method to understand complex medical information, patients could make more informed decisions about their care. This technology has the potential to enhance patient outcomes and enhance the general quality of care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mixed reality is a robust tool for medical education and training. While VR has its limitations, MR offers a more immersive and interactive method to study complex anatomical structures. By leveraging this technology, medical educators can create a more engaging and effective learning experience for his or her students. Additionally, using MR in patient education has the potential to enhance patient outcomes and enhance the standard of care. As this technology continues to evolve, it would be exciting to see the impact it has on the sector of medication.